Python note 1 lists to store and retrieve data
When you have a large amount of data, it becomes difficult to store and retrieve it whenever you want. Python has some inbuilt functionalities and lists that make this task easier for you. We create two lists, bob, and sue.
Here are two records to represent two people. These are lists of four properties, name, age, pay, and job fields.
How to access a field in a list?
You can access it by position. Then you can also perform many operations on the items of the list.
For example, 'Bob Smith' is a string and you can split the string within the list.
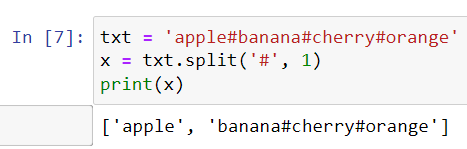
How to split a string?
split() method splits a string into a list.
separator: space is the default separator. But, we can also specify the separator
syntax
string.split(separator, maxsplit)
separator is optional. maxsplit is also optional. It specifies the number of splits. Default value is -1 which means all the occurrences.
Using a separator
Using maxsplit
Here is how the algorithm works
bob[0]
It calls an element Bob Smith.
bob[0].split()
It splits string bob[0] which is 'Bob Smith' into a sublist, ['Bob', 'Smith'] within the list, bob.
bob[0].split is a list and [-1] is its index.
Negative indexing in python
Negative indexing starts from the right end.
positive indexing goes this way: 0, 1, 2, 3, 4
negative indexing goes this way: -5, -4, -3, -2, -1
Indexing for the sublist, [Bob, Smith] is
-2, -1
We can use the split method only for strings.
We can also increase the salary of Sue in this manner.
Notice how the value of the salary has been changed in the list.
A Database List
We can create a single list, people, and combine bob and sue lists into it.
Person is the iterant.
Fetching specific records in loops
We will use people to call Sue Jones.
bob[0]= 'Bob Smith'
and
sue[0]= 'Sue Jones'
split()
creates sublits within the sublists, bob and sue.
bob[0],split()= ['Bob', 'Smith']
-2 -1
sue[0].split()= ['Sue', 'Jones']
-2 -1
So,
bob[0].split()[-1]= 'Smith'
sue[0].split()[-1]= 'Jones'
person iterates over bob and sue sublists.
[2] means third elment from each sublist.
*=1.2 means multiplied by 1.2.
List comprehension maps, and generator expressions
We will create a list of salaries for all people using the in-built functions of python.
Explanation
pays is the name of a new list.
person[2] is the iterant calling third element in each sublist.
person iterates over each sublist.
people is the name of the list.
Map() function in python
The map() function executes a aspecicified function for each itrem in an iterable. the item is sent to the function as a parameter.
Syntax
map(function, iterables)
function is compulsory. It tells whatt to perform for each item.
Iterable is compulsory. It is a sequence, collection, or an iterable object. Many iterables can also be passed. The function should have one parameter for each iterable.









Comments
Post a Comment